As organizations generate more data than ever before, the challenge is no longer access – it’s insight. Augmented Analytics in SAP Analytics Cloud bridges this gap by combining automated machine learning with intuitive business intelligence tools.
Specifically, with Smart Predict, SAC empowers business users to forecast outcomes, identify trends, and make decisions backed by predictive insights – without needing data science expertise. In this post, we’ll therefore explore how predictive modeling works in SAC, how to prepare your data, and how to use predictive outputs effectively across stories and planning models.
Understanding the Data Lifecycle in Smart Predict
Predictive analytics begins and ends with data. In SAC, datasets flow through several stages – training, application, and output – each serving a unique role in model creation and prediction.
Training Dataset: Learning from the Past
The training dataset is the foundation of your predictive model. It essentially contains past observations where the target variable (for example, customer churn, revenue, or sales volume) is already known.
Smart Predict studies this dataset to uncover relationships between the target and other variables, known as influencers, and builds a model capable of predicting future outcomes.
Application Dataset: Applying the Model
Once trained, the model is ready to be used on an application dataset – new data structured in exactly the same way as the training set:
- Same variable names
- Same order
- Same number of columns
This consistency ensures that the model can correctly interpret and predict based on the new data.
Output Dataset: Getting the Predictions
When the model is applied, SAC generates an output dataset containing predicted values for the target variable, along with optional confidence levels or additional metrics.
By default, the file is stored in Main Menu → Browse → Files, although users can choose a different location.
Structuring Data for Predictive Scenarios
Every predictive scenario in SAC requires a properly formatted dataset.
Let’s look at how this structure differs across common predictive model types.
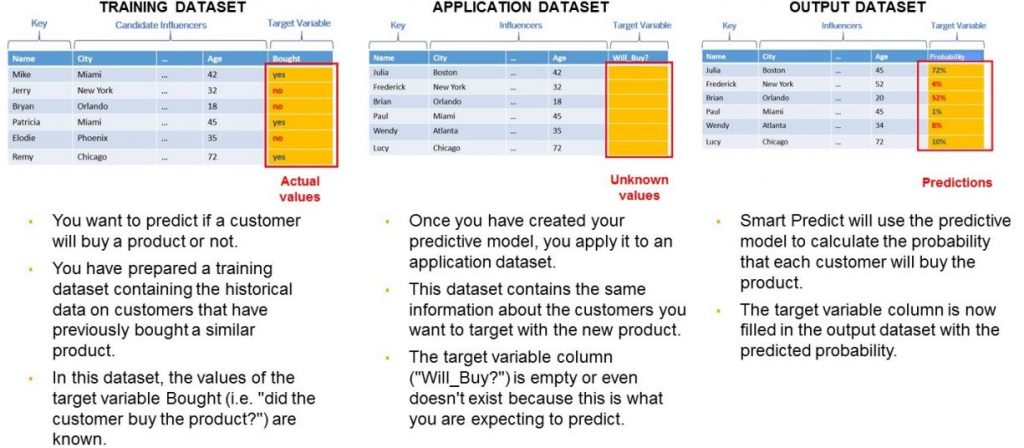
Classification and Regression Models
These models require:
- One target variable (e.g., “Customer will churn: Yes/No”)
- Multiple influencer variables (e.g., customer age, spend, contract length)
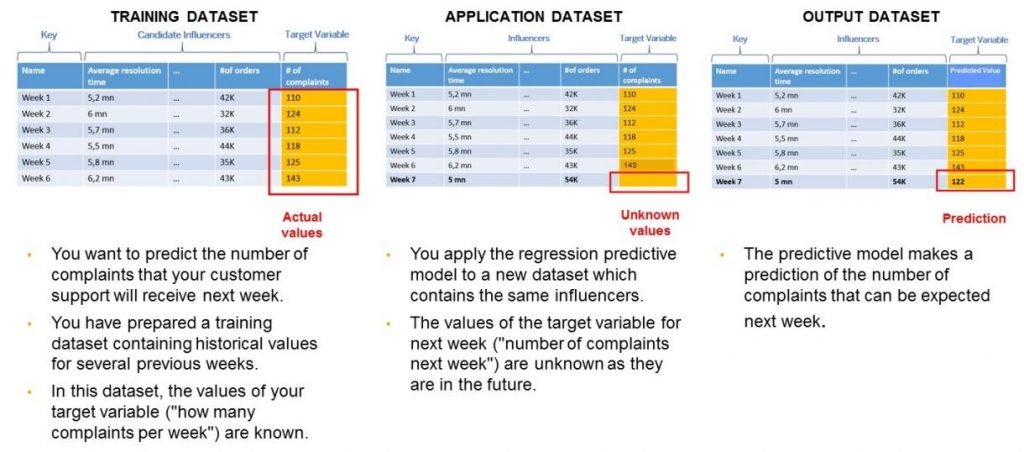
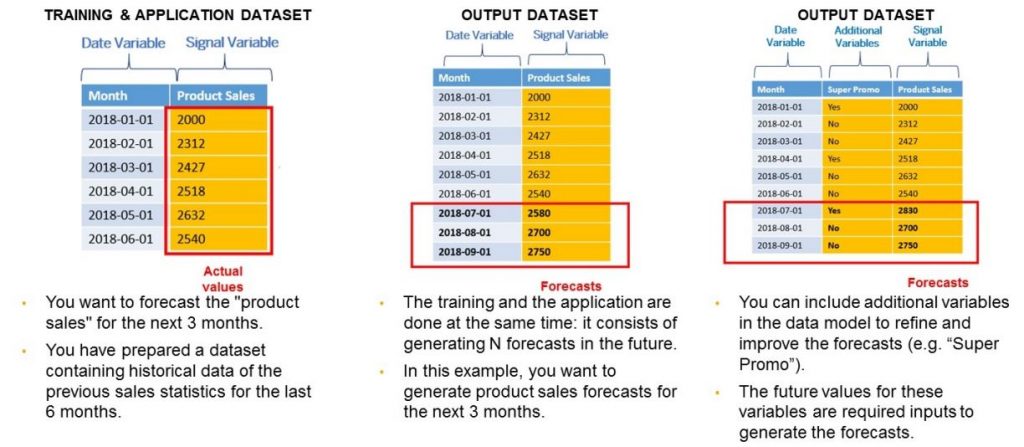
Time Series Models
For time-dependent forecasts, your dataset must include:
- A date column (accepted formats: YYYY-MM-DD, YYYY/MM/DD, etc.)
- A signal variable (the value to forecast)
- Optional influencer variables to improve prediction accuracy
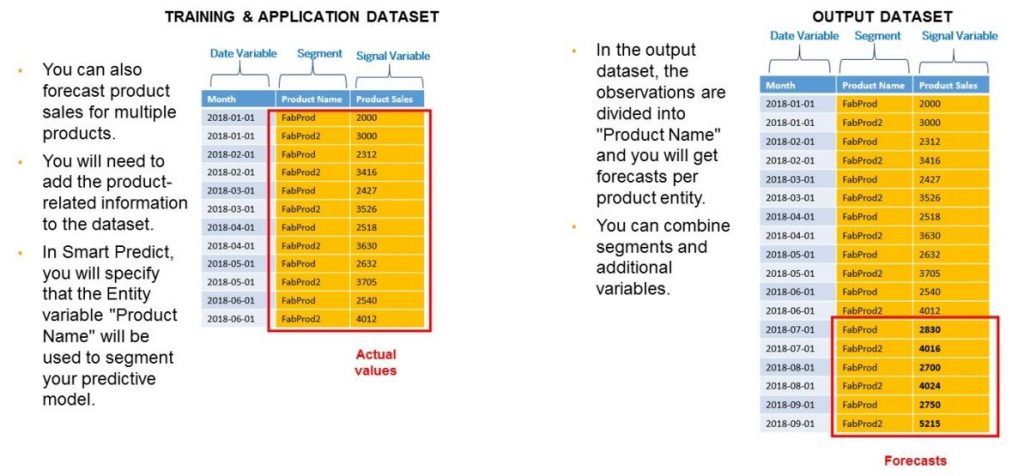
Segmented Time Series Models
In segmented time series, you forecast for multiple groups simultaneously – such as products, stores, or regions.
To do this, add a segment column to distinguish between these series.
Consuming Predictive Outputs in SAP Analytics Cloud
Creating predictions is only half the journey – indeed, the real value lies in how you consume and apply them. SAC provides flexible options for both acquired and live datasets.
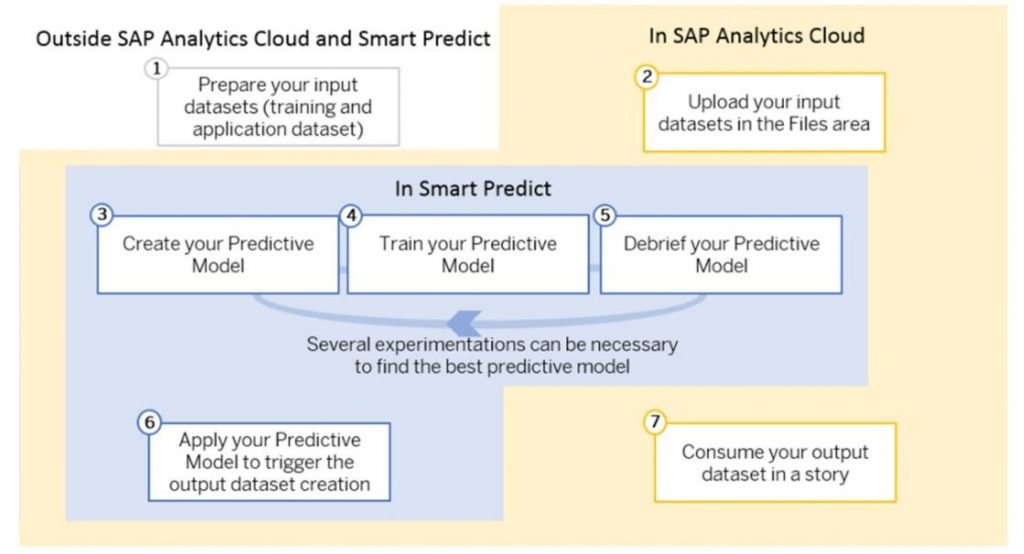
Using Predictions from Acquired Datasets
For acquired datasets, the output can be:
- Loaded directly into a story, automatically becoming an embedded model
- Converted into a dedicated SAC model for sharing and collaboration
However, keep in mind that SAC only processes the first 100 columns of an output dataset.
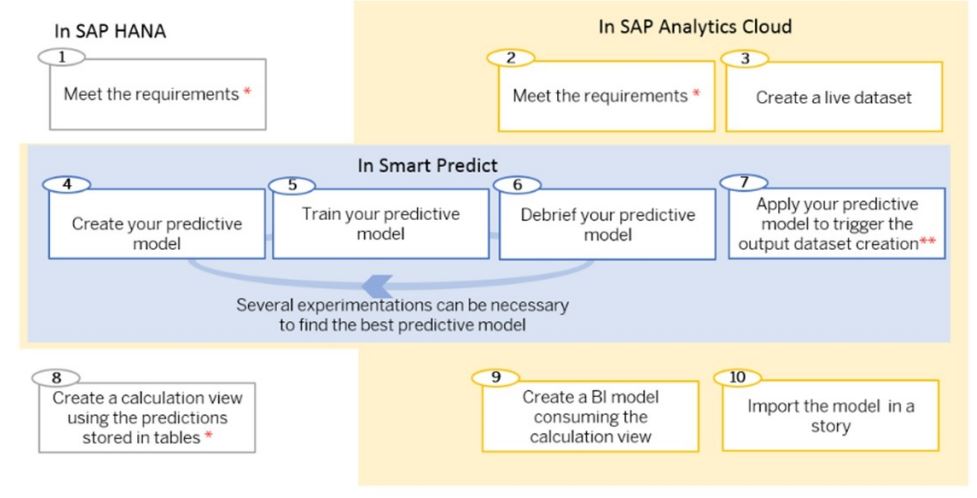
Using Predictions from Live Datasets
When working with live data connections (such as SAP HANA):
- Go to Create → Model in SAC
- Choose Get data from a datasource → Live Data Connection
- Select SAP HANA as the system type and specify the calculation view
- Build your story using this live model as the source
This way, you can analyze live predictions without data duplication.
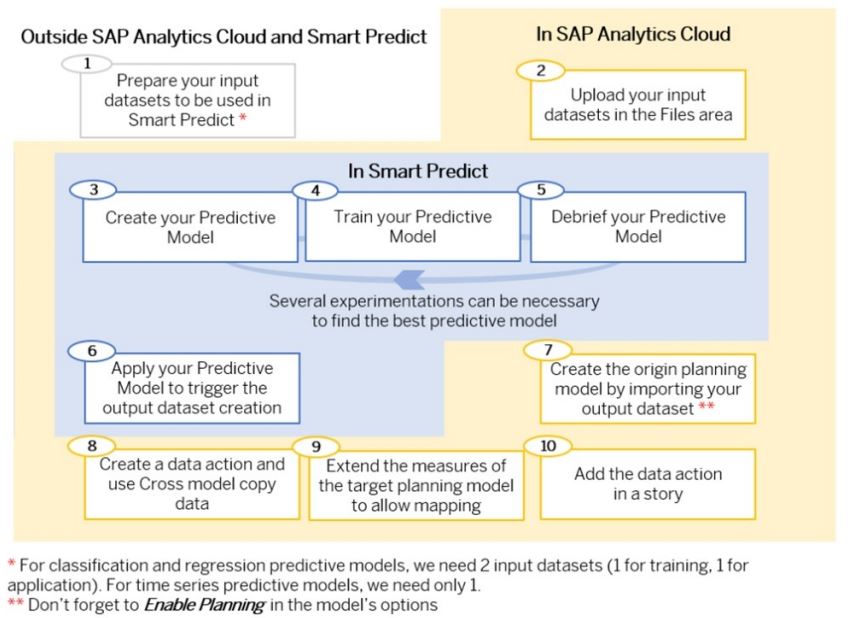
Integrating Predictions into Planning Models
Predictive planning is also available in SAC, enabling you to:
- Create a planning model to include Smart Predict outputs
- Design a Data Action to copy predictions into your main planning model
- Trigger this action in your planning story to merge predictive and actual data
This integration transforms planning into a proactive, insight-driven process.
Predictive Modeling in Action: Two Key Phases
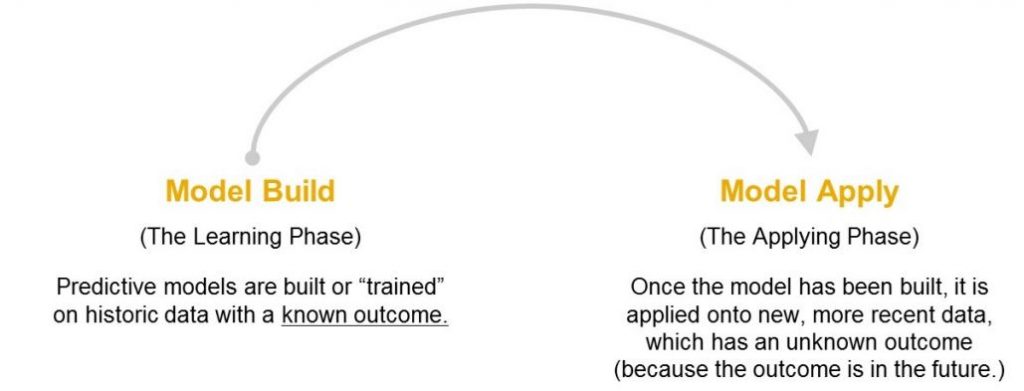
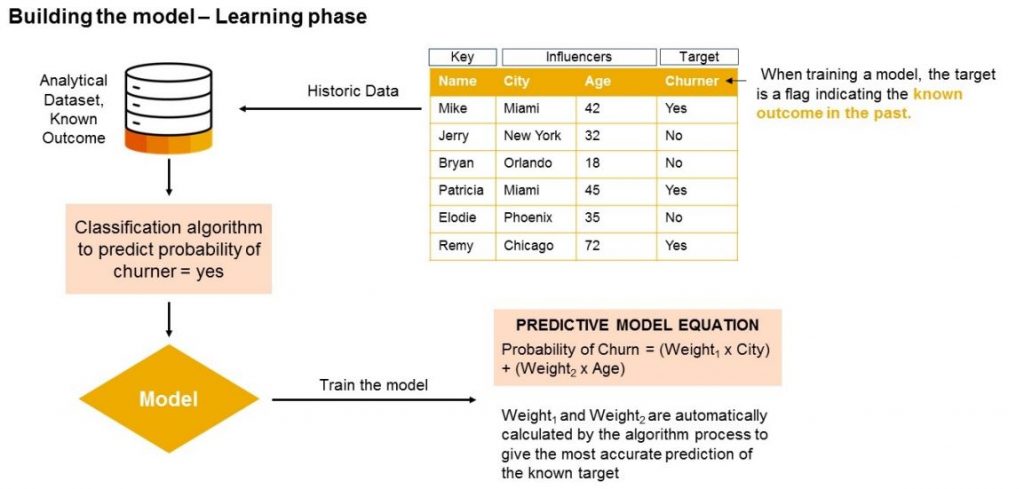
Model Build – Learning Phase
In this phase, Smart Predict analyzes historical data to identify patterns.
For instance, a telecom company might use past data (January-March) to predict customer churn in April.
SAC automatically divides data into:
- Training subset (75%) – for model learning
- Validation subset (25%) – for model testing
Time-series models use the same split but follow the chronological order of data
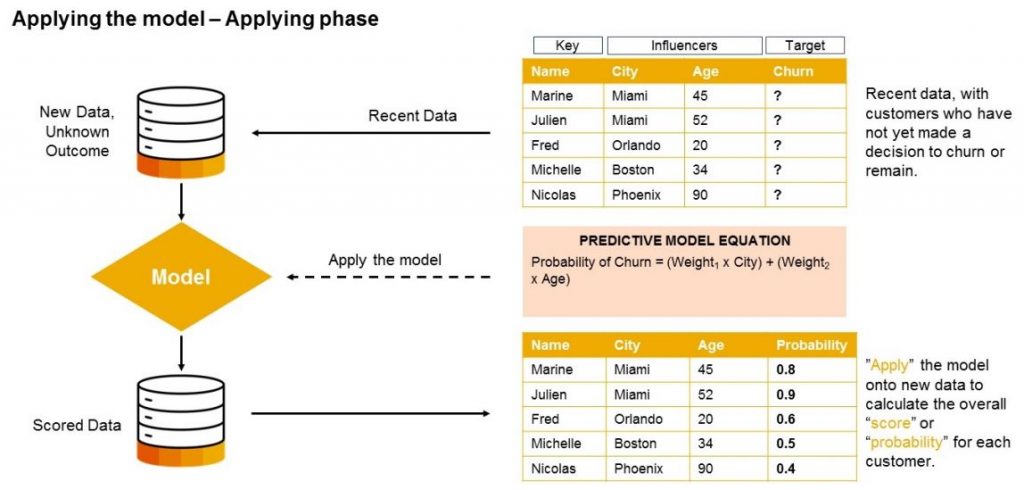
Model Apply – Applying Phase
After learning, the model is ready to make real-world predictions on new or upcoming data.
These predictions can then be embedded in dashboards, shared across departments, or integrated into planning workflows.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Leaker Variables
A critical rule in predictive modeling is to avoid leaker variables – fields that contain information unavailable at prediction time. Leaker variables create artificially high accuracy and unreliable models.
To detect them:
- Review the Influencer Contributions report
- Watch for variables with unusually strong correlations to the target
- Exclude variables created or updated after the target’s time frame
If your model seems too perfect, it might be too good to be true – and likely leaking.
Bringing It All Together
Smart Predict in SAP Analytics Cloud simplifies predictive analytics by automating complex modeling tasks, structuring data intelligently, and integrating predictions seamlessly into business stories and planning workflows.
When used correctly, it helps organizations move from descriptive analytics (“What happened?”) to predictive intelligence (“What will happen next?”) – empowering faster, smarter, and more confident decision-making.
Final Thoughts
Augmented Analytics is more than a trend – it’s a transformation in how businesses approach data. By understanding the data structure, modeling process, and output consumption in SAP Analytics Cloud, you can unlock powerful predictive capabilities that turn raw information into actionable foresight.
With the right foundation and a careful approach to data quality, your organization can truly embrace the future of data-driven decision-making.
Next, we’ll dive into Classification Models in SAP Analytics Cloud, showing how to connect to live data, build a model, and apply it with Smart Predict.
