Consolidation Extensions’ Account Configuration Guide
The Account Configuration Guide serves as a preconfigured administrative tool designed to guide users with specific roles to effectively manage various groups of accounts, such as: Intercompany, Investment, Capital, Retained Earnings and Non-controlling Interest (NCI), Profit and Loss Treatment, Dividends Paid/Received, and Equity Method – Associates. Users can assign specific elimination rules to the accounts in structured process, mitigating risk of erroneous configuration.
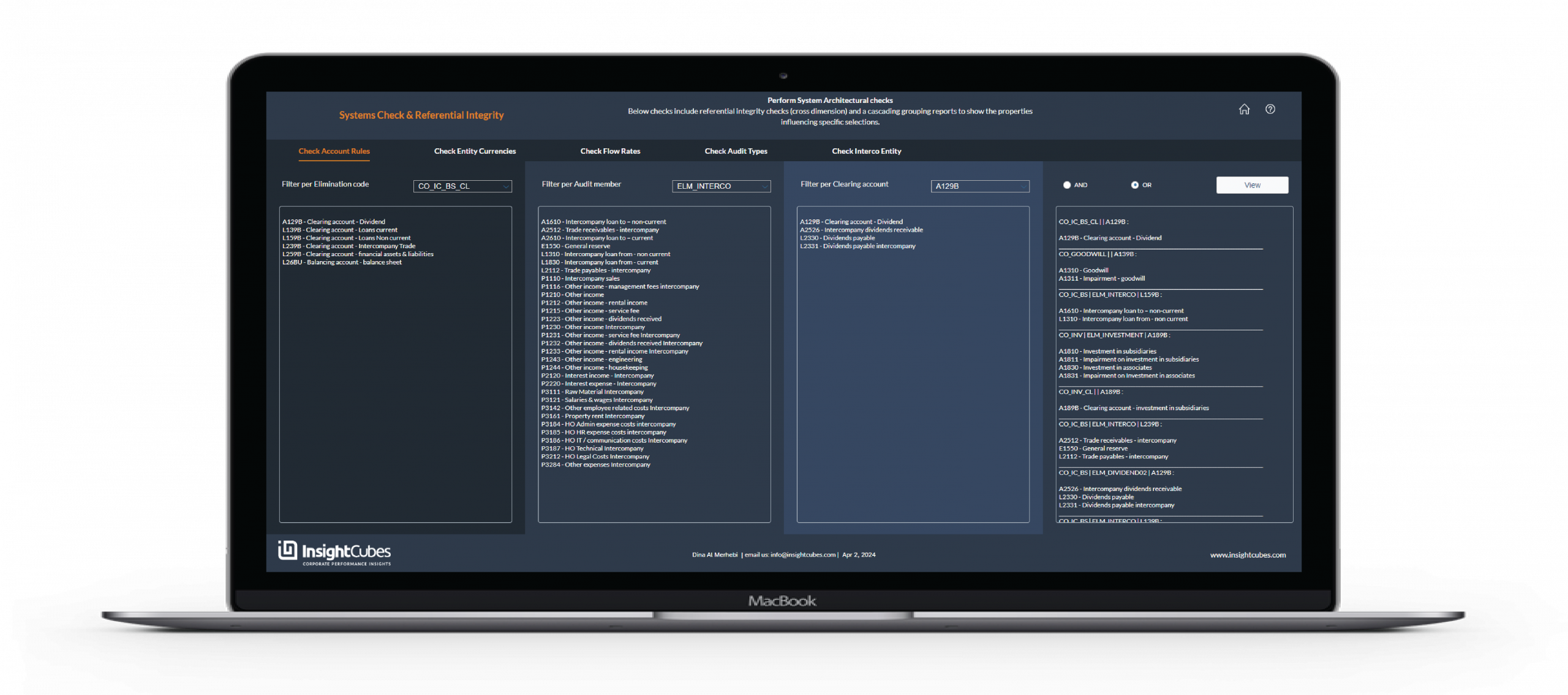
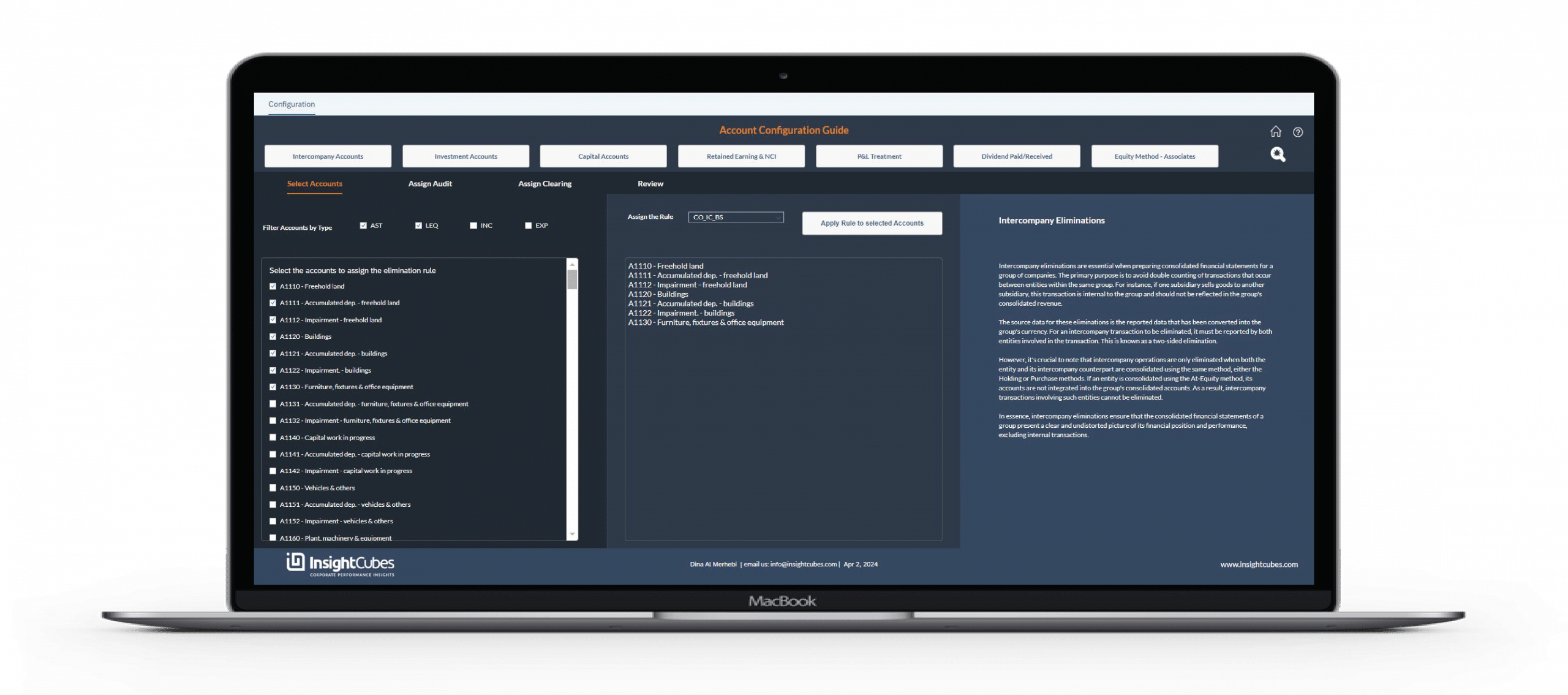
The configuration starts when the user selects the automated elimination type from the button list, then the specific accounts subject to the elimination rule. Additionally, the user can filter the list of available accounts based on account type (Asset, Liability, Equity, Income, Expense). Once the desired accounts are selected, the assignment of the rule to the selected accounts can be applied from a dropdown menu and then clicking the “Apply Rule to Selected Accounts” button.
For each of the selected accounts, the user can assign the receiving Audit Trail member of the automated elimination results based on the rule, and if applicable, the clearing account.
Account categories and their associated rules:
1- Intercompany Accounts
Intercompany eliminations are essential when preparing consolidated financial statements for a group of companies. The primary purpose is to avoid double counting of transactions that occur between entities within the same group. For instance, if one subsidiary sells goods to another subsidiary, this transaction is internal to the group and should not be reflected in the group’s consolidated revenue.
The source data for these eliminations is the reported data that has been converted into the group’s currency. For an intercompany transaction to be eliminated, it must be reported by both entities involved in the transaction. This is known as a two-sided elimination.
However, it’s crucial to note that intercompany operations are only eliminated when both the entity and its intercompany counterpart are consolidated using the same method, either the Holding or Purchase methods. If an entity is consolidated using the At-Equity method, its accounts are not integrated into the group’s consolidated accounts. As a result, intercompany transactions involving such entities cannot be eliminated.
In essence, intercompany eliminations ensure that the consolidated financial statements of a group present a clear and undistorted picture of its financial position and performance, excluding internal transactions.
By default, the CO_IC_BS rule will be assigned to the balance sheet intercompany accounts and CO_IC_PL will be assigned to the Profit and Loss intercompany accounts.
- CO_IC_BS
- CO_IC_PL
- RULE010
- RULE011
- RULE012
2- Investment Accounts
When a parent company holds ownership in a subsidiary, it logs the value of this investment as an asset on its individual balance sheet. In this step, you need to identify the Investment account(s) that contains the investment breakdown between the holding companies and their respective subsidiaries and affiliates. By default, the CO_INV rule will be assigned to the investment accounts.
- CO_INV
- RULE020
- RULE021
- RULE022
3- Capital Accounts
Elimination of capital accounts is done with a knock-off against the investment value of the holding company in the subsidiary. This is a rule, like the Investment Elimination, applicable to holding companies and their subsidiaries; affiliates are not subject to this rule.
In this configuration, the user needs to select the Capital accounts subject to elimination against the investment value from holding company’s books. In case the investment value in Holding Company’s books is different than the set of Capital Accounts of the subsidiary being eliminated, a clearing account can be used to show the differences or further utilize in goodwill or NCI/RE adjustments.
- CO_EQUITY1
- RULE030
- RULE031
- RULE032
By default, CO_EQUITY1 will be applied to the set of Capital Accounts subject to full elimination.
4- Retained Earning and NCI
Retained earnings and Non-Controlling Interest (NCI) represent two important components of a company’s equity. Retained earnings refer to the portion of a company’s net income that is kept or retained within the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. They represent the cumulative profits or losses of the company since its inception, minus any dividends paid out to shareholders.
Non-Controlling Interest (NCI), on the other hand, refers to the portion of equity in a subsidiary company that is not owned by the parent company. It represents the ownership stake held by external shareholders or minority investors in the subsidiary.
NCI is reported separately on the consolidated financial statements to distinguish it from the equity attributable to the parent company’s shareholders.
- CO_EQUITY2
- RULE040
- RULE041
- RULE042
By default, CO_EQUITY2 is assigned to the Retained Earning account, and the clearing account of the Retained Earnings should point to the NCI account.
6- Dividends Paid/Received
Dividends paid and received refer to the distribution of earnings by a company to its shareholders. When a company pays dividends, it distributes a portion of its profits to its shareholders as a return on their investment. Alternatively, when a company receives dividends, it earns income from its investments in other companies’ stocks. Dividends paid and received are recorded in the financial statements as outflows and inflows of cash. Not to be confused with Dividends payables/receivables, the dividends paid/received will be subject to three leg eliminations, covering the dividends paid/received from the P&L side, the Retained Earning from the Equity Side (on specific flow/F06/Dividends paid/received) and investment from the asset side.
- CO_DIVIDENDS
- RULE060
- RULE061
- RULE062
By default, CO_DIVIDENDS is applied to the P&L dividends paid/received accounts.
7- Equity Method/Associates
The equity method and associates refer to the accounting treatment used when a company holds significant influence, but not control, over another company. Under the equity method, the investing company recognizes its investment in the associate on its balance sheet and adjusts it periodically to reflect its share of the associate’s profits or losses and dividends received. Associates are companies in which the investing company holds between 20% and 50% of the voting shares and are accounted for using the equity method rather than consolidation. This method allows the investing company to accurately reflect its economic interest in the associate’s financial statements.
- EM_CO_EQUITY1
- EM_CO_EQUITY2
- EM_CO_INV
- RULE100
- RULE101
- RULE102
If the same investment account is used to register investment in affiliates and investment in subsidiaries, this step can be omitted, since the system will automatically detect the ownership method.